What Is a Lipid Profile?
A lipid profile is a blood test that measures several key indicators of fat metabolism. It is used to assess the risk of atherosclerosis, heart attack, and stroke.
- Total cholesterol
- LDL — low-density lipoprotein ("bad" cholesterol)
- HDL — high-density lipoprotein ("good" cholesterol)
- Triglycerides
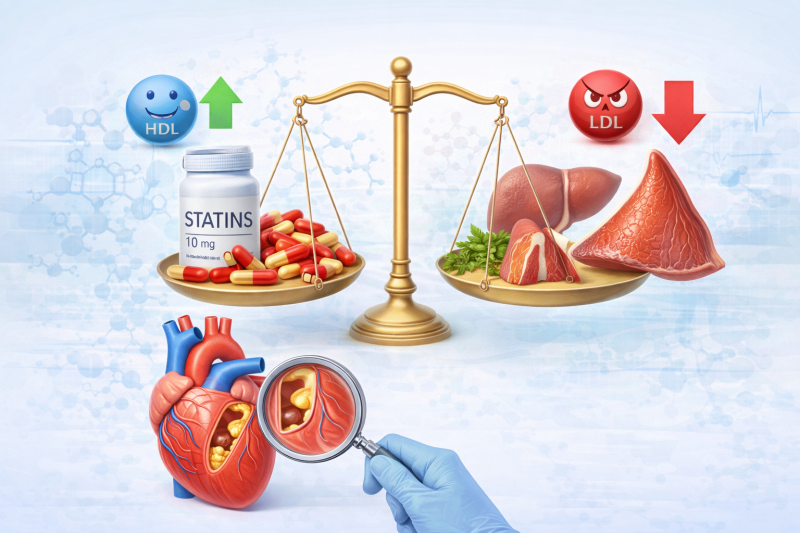
LDL — The "Bad" Cholesterol
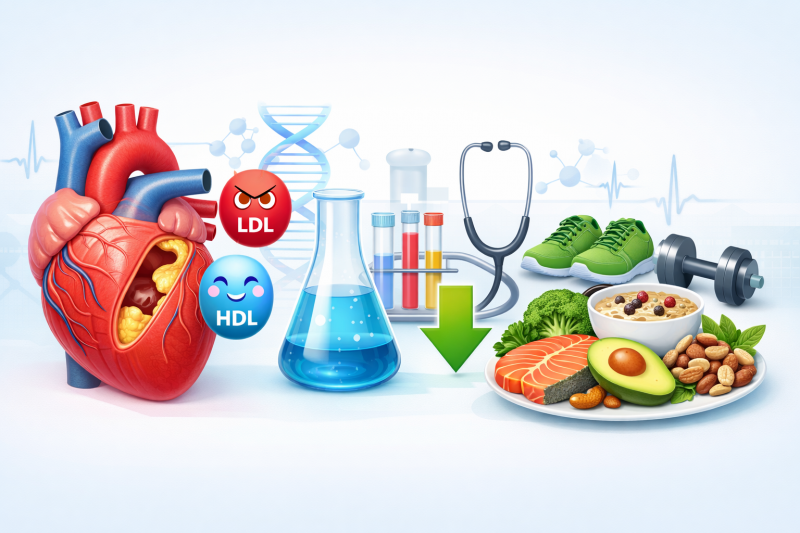
LDL carries cholesterol from the liver to body tissues. Excess LDL can accumulate in artery walls, forming atherosclerotic plaques.
High LDL levels are strongly associated with an increased risk of heart attack and stroke.
HDL — The "Good" Cholesterol
HDL plays a protective role by transporting excess cholesterol back to the liver for elimination.
Higher HDL levels are linked to a lower cardiovascular risk.
Triglycerides
Triglycerides are a form of stored energy. Elevated levels are often associated with excess calories, sugar, and alcohol intake.
High triglycerides increase the risk of metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease.
Why the Whole Profile Matters
Even with normal total cholesterol, high LDL or low HDL can pose a risk. That is why healthcare professionals evaluate the entire lipid profile.
Conclusion
A lipid profile is more than just numbers — it is a valuable tool for assessing vascular health. Understanding LDL, HDL, and triglyceride values helps guide lifestyle changes and reduce long-term cardiovascular risk.